 Sedition Act (1798) Sedition Act (1798) |
|
This is one of four acts known collectively as the Alien and Sedition Acts. These acts were passed by a Federalist-controlled Congress applied restrictions to immigration and speech in the U.S. They were highly controversial and contributed to the Federalist defeat in the election of 1800. After 1802, only the Alien Enemies Act remained in force, and has continued to be invoked during times of war. The Sedition Act made it illegal to print "false, scandalous and malicious writing" against the U.S. government. It was used to suppress speech critical of the Federalist Party.
|
 Selective Service Act (1917) Selective Service Act (1917) |
|
This act authorized the U.S. government to raise a national army through compulsory enlistment via a draft. The military was segregated at the time of World War I, and Black soldiers were mostly relegated to labor roles.
|
 Selective Training and Service Act (1940) Selective Training and Service Act (1940) |
|
This act authorized the U.S. government to raise a national army through compulsory enlistment via a draft. While the act prohibited discrimination based on race, the military was still segregated at the time of World War II, and Black soldiers were mostly relegated to labor roles.
|
 Shelby County v. Holder (2013) Shelby County v. Holder (2013) |
|
This landmark Supreme Court decision overturned the federal pre-clearance section the Voting Rights Act of 1965 which required jurisdictions to seek approval from the Department of Justice or the U.S. District Court for D.C., before making changes to their voting laws. This decision limited the federal government's ability to protect voting rights for all citizens and has since allowed policies such as voter ID laws and the closing polling locations to limit voting rights for certain groups.
|
 Somerset v. Stewart (1772) Somerset v. Stewart (1772) |
|
This case heard before the English Court of King's Bench determined that slavery was unsupported by English Common Law and that no enslaved person could be forced out of England to be sold into slavery. James Sommerset was an enslaved person who had been purchased by Charles Stewart in Boston, Massachusetts, then taken to England. Sommerset later escaped, and Stewart had him captured and imprisoned on a ship headed to Jamaica. Sommerset's godparents applied for a writ of habeas corpus. Following the court’s decision, enslaved people in the American Colonies filed freedom suits based on Mansfield's ruling.
|
 Stamp Act (1765) Stamp Act (1765) |
|
The Stamp Act placed a tax on various printed material like legal documents, playing cards, and newspapers. The act specifies skins and pieces of parchment serving various legal roles and the differing amounts of tax each document needed. The tax’s payment was confirmed by the placement of a stamp indicating a specific amount on the good. It was the first of a series of taxes placed on the North American colonies without their consent, sparking protest and resistance.
|
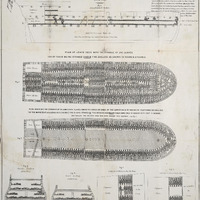 Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) |
|
This image was used by English abolitionists to demonstrate the terrible conditions aboard slave ships.
|
 Students for Fair Admission v. Harvard (2023) Students for Fair Admission v. Harvard (2023) |
|
This Supreme Court case considered whether Harvard's admissions process violated Title VI of the Civil Rights Act. The Court decided that the race-based admissions system did not meet the strict scrutiny required to allow a race-based system, and held as unconstitutional the consideration of an applicant’s race as a factor in making an admissions decision that benefits diversity.
|
 Studying the Missing and Murdered Indian Crisis Act of 2019 Studying the Missing and Murdered Indian Crisis Act of 2019 |
|
This bill was introduced to authorize the Government Accountability Office to collect data and study the crisis of missing and murdered Native Americans. It did not pass into law, but was a part of a broader legislative effort to bring awareness to murdered and missing Indigenous People.
|
 Sugar Act (1764) Sugar Act (1764) |
|
The Sugar Act of 1764 imposed duties on sugar, molasses, wine, and other goods imported to United States colonies. The act also includes expectations of stricter adherence to trade regulations and steeper penalties for violations. It even includes a provision to defend those enforcing the act. It was part of a series of bills imposing unequal tariffs on North American colonies and those in England. These policies aided in the popularity of independence movements in North America.
|
 Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) |
|
In this sworn affidavit, Alexander Harlin attested that he, as a "Choctaw Freedman, of African Blood," was enslaved by a Choctaw woman Sarah Harlin until the Treaty of 1866 was signed. The statement was made in support of his application for enrollment in the Choctaw Nation under the Act of June 10, 1896 which authorized the Dawes Commission to add names to existing tribal rolls.
|
 Tea Act (1773) Tea Act (1773) |
|
The Tea Act created a monopoly on the tea trade for the East India Company. It ultimately lowered tea prices in Britain but forced colonists to pay the Townshend tax on tea. Reactions to the Act sparked the Boston Tea Party. Prior to the Tea Act, the East India Company was required to sell tea directly to London and then other merchants would sell tea to the colonies. The Tea Act eliminated third party merchants and forced colonists to buy taxed tea.
|
 Terry v. Ohio (1968) Terry v. Ohio (1968) |
|
Terry v. Ohio is the landmark Supreme Court case that established the basis for stop and frisk policies. These policies disproportionately affect Black people and lead to the disproportionate incarceration of Black Americans.
|
 The Carceral State: Legal Histories of American Unfreedom The Carceral State: Legal Histories of American Unfreedom |
|
This teaching module discusses race, the carceral state, and the criminalization of Blackness, featuring a webinar with legal historian Taja-Nia Henderson.
|
 The Insular Cases and Contested Citizenship The Insular Cases and Contested Citizenship |
|
This teaching module discusses the intersection of U.S. colonial power and migration, featuring a webinar with Robert McGreevey, author of the 2018 book, Borderline Citizens: The United States, Puerto Rico, and the Politics of Colonial Migration.
|
 The Woman Suffrage Movement and Frederick Douglass (1908) The Woman Suffrage Movement and Frederick Douglass (1908) |
|
In this speech given on the 60th Anniversary of the Seneca Falls Convention, Black women's rights advocate Mary Church Terrell reflects on the role of Frederick Douglass in the women's suffrage movement.
|
 The Worst Trickster Story Ever Told: Native America, the Supreme Court, and the U.S. Constitution The Worst Trickster Story Ever Told: Native America, the Supreme Court, and the U.S. Constitution |
|
This teaching module looks the Supreme Court's understanding of Native America from an Indigenous perspective, featuring a webinar with Keith Richotte, Jr., author of the 2025 book, The Worst Trickster Story Ever Told: Native America, the Supreme Court, and the U.S. Constitution.
|
 Townshend Revenue Act (1767) Townshend Revenue Act (1767) |
|
The Townshend Acts were a series of taxes and regulations imposed on the American colonies by the British Parliament. The Townshend Revenue Act levied taxes on glass, lead, tea, and paper, replacing the Stamp Act, which was repealed the year before.
|
 Treaty of Amity, Commerce and Navigation (1794) Treaty of Amity, Commerce and Navigation (1794) |
|
Unpopular with the American public, this treaty between the United States and Britain attempted to resolve outstanding issues from American independence. This treaty, also known as John Jay’s Treaty, made trade between the two countries more even and reduced British military presence in the U.S.
|
 Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1768) Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1768) |
|
This treaty is the first formal treaty between the British and the Six Nations following the French and Indian War. Large amounts of Native American land were ceded to the British as a result of this treaty.
|
 Treaty of Paris (1783) Treaty of Paris (1783) |
|
The Treaty of Paris was signed by the United States and Britain in 1783 to end the American War for Independence (1775- 1783). It recognized the United States as an independent state and delineated the Western boundaries of the new country.
|
 Trump v. Hawaii (2018) Trump v. Hawaii (2018) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court ruled that the travel ban instituted by President Trump's Executive Order 13780 was within presidential power granted by Section 212(f) of the Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965.
|
 Trump v. United States (2024) Trump v. United States (2024) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court ruled that a president "may not be prosecuted
for exercising his core constitutional powers" and is entitled to "a presumptive immunity from prosecution for all his official acts."
|
 Tydings–McDuffie Act (1934) Tydings–McDuffie Act (1934) |
|
This act established the process for the independence of the Philippine Islands, then a U.S. territory, after a ten-year transition period. The act reclassified Filipinos them from U.S. nationals to aliens and limited the number of immigrants from the Philippines to 50 per year.
|
 U.S. Constitutionalism and Native American Sovereignty U.S. Constitutionalism and Native American Sovereignty |
|
This teaching module discusses the centrality of Native people and their nations throughout American history, featuring a webinar with Ned Blackhawk, author of the 2023 book, The Rediscovery of America: Native Peoples and the Unmaking of U.S. History.
|
 Sedition Act (1798)
Sedition Act (1798) Selective Service Act (1917)
Selective Service Act (1917) Selective Training and Service Act (1940)
Selective Training and Service Act (1940) Shelby County v. Holder (2013)
Shelby County v. Holder (2013) Somerset v. Stewart (1772)
Somerset v. Stewart (1772) Stamp Act (1765)
Stamp Act (1765) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788)
Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Students for Fair Admission v. Harvard (2023)
Students for Fair Admission v. Harvard (2023) Studying the Missing and Murdered Indian Crisis Act of 2019
Studying the Missing and Murdered Indian Crisis Act of 2019 Sugar Act (1764)
Sugar Act (1764) Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896)
Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Tea Act (1773)
Tea Act (1773) Terry v. Ohio (1968)
Terry v. Ohio (1968) The Carceral State: Legal Histories of American Unfreedom
The Carceral State: Legal Histories of American Unfreedom The Insular Cases and Contested Citizenship
The Insular Cases and Contested Citizenship The Woman Suffrage Movement and Frederick Douglass (1908)
The Woman Suffrage Movement and Frederick Douglass (1908) The Worst Trickster Story Ever Told: Native America, the Supreme Court, and the U.S. Constitution
The Worst Trickster Story Ever Told: Native America, the Supreme Court, and the U.S. Constitution Townshend Revenue Act (1767)
Townshend Revenue Act (1767) Treaty of Amity, Commerce and Navigation (1794)
Treaty of Amity, Commerce and Navigation (1794) Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1768)
Treaty of Fort Stanwix (1768) Treaty of Paris (1783)
Treaty of Paris (1783) Trump v. Hawaii (2018)
Trump v. Hawaii (2018) Trump v. United States (2024)
Trump v. United States (2024) Tydings–McDuffie Act (1934)
Tydings–McDuffie Act (1934) U.S. Constitutionalism and Native American Sovereignty
U.S. Constitutionalism and Native American Sovereignty