 Roberto Alvarez, et al. v. E. L. Owen, et al. (1931) Roberto Alvarez, et al. v. E. L. Owen, et al. (1931) |
|
This case was the first successful school desegregation case in the United States, decided fifteen years before Brown v. Board of Education. When the school board in Lemon Grove, California, attempted to build a separate school for students of Mexican origin, the court ruled that the segregation violated state laws which considered people of Mexican descent to be white.
|
 Seminole Agreement (1900) Seminole Agreement (1900) |
|
This congressional act ratified an agreement with the Seminole Nation concerning allotment, like enrollment and laws of descent. The second proviso established matrilineal descent of lands, money, and property for heirs.
|
 State of Nebraska, ex rel. Daniel Freeman, v. John Scheve et al. (1902) State of Nebraska, ex rel. Daniel Freeman, v. John Scheve et al. (1902) |
|
In this case, Daniel Freeman, recognized as the first homesteader under the 1862 Homestead Act, made a public grievance over the use of the Bible in a public school near Beatrice. When the teacher refused to cease using the Bible, offering prayers, and singing hymns in her classroom, Freeman took his case to the school board, who defended the teacher. He then took his case to the courts. The lower court also sided with the teacher, and he appealed the case to the Nebraska Supreme Court. The higher court found that the actions of the teacher and the school board violated the provisions in Nebraska's constitution regarding the separation of church and state. The U.S. Supreme Court did not make a similar ruling until 1962 in Engel v. Vitale.
|
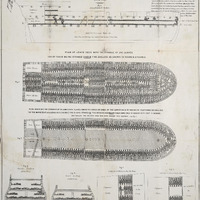 Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) |
|
This image was used by English abolitionists to demonstrate the terrible conditions aboard slave ships.
|
 Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971) Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court addressed busing as a means of integrating schools. After a federal district court found that the North Carolina school system's zoning-based desegregation plan was ineffectual, the court appointed an expert to develop an alternative plan. The new plan required the busing of students to various schools in order to achieve desegregation, which the Supreme Court held as an acceptable "remedial technique" to that end. The decision was eventually abrogated in Belk v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (2002), where the court found that the previously instituted remedial techniques had been successful and were no longer necessary.
|
 The Five Civilized Tribes Act (1906) The Five Civilized Tribes Act (1906) |
|
This act legislated the end of tribal enrollment in the Five Tribes, as well as the dissolution of their tribal government. However, section 28 extended tribal sovereignty for the Five Tribes for a truncated 30 days per year.
|
 Universal Access to Child Care Fact Sheet (2025) Universal Access to Child Care Fact Sheet (2025) |
|
In 2025, New Mexico became the first state in the nation to guarantee no-cost universal child care, regardless of income.
|
 Yarborough v. Alvarado (2004) Yarborough v. Alvarado (2004) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court overturned a Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals ruling that stated that youth and inexperience with law enforcement should be accounted for when evaluating custody. In the majority opinion, the Supreme Court held that previous rulings had rejected reliance on factors such as age and inexperience in custody analysis.
|
 Roberto Alvarez, et al. v. E. L. Owen, et al. (1931)
Roberto Alvarez, et al. v. E. L. Owen, et al. (1931) Seminole Agreement (1900)
Seminole Agreement (1900) State of Nebraska, ex rel. Daniel Freeman, v. John Scheve et al. (1902)
State of Nebraska, ex rel. Daniel Freeman, v. John Scheve et al. (1902) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788)
Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971)
Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971) The Five Civilized Tribes Act (1906)
The Five Civilized Tribes Act (1906) Universal Access to Child Care Fact Sheet (2025)
Universal Access to Child Care Fact Sheet (2025) Yarborough v. Alvarado (2004)
Yarborough v. Alvarado (2004)