 Remembering a dark past, renewing resolve for the future (2019) Remembering a dark past, renewing resolve for the future (2019) |
|
This article from the Omaha World Herald describes Omaha's official observance of the 100-year anniversary of the lynching of Will Brown. Omaha Mayor, Jean Stothert, spoke at the commemoration calling Will Brown's lynching one of the darkest days in our history.
|
 Rights of Black Men (1791) Rights of Black Men (1791) |
|
This commentary was written by Connecticut anti-slavery advocate Abraham Bishop in support of the Haitian Revolution. Bishop's work was printed in the Boston newspaper, The Argus.
|
 Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810) Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810) |
|
Seamen's Protection Certificates were documents authorized by an act of Congress in 1796 to protect U.S. sailors from being impressed into the service of foreign navies. For Black Americans, they also served as a way to document their free status. This certificate was issued for James Forten Dunbar, a free man of mixed ancestry who spent a long career at sea as a sailor and sail-maker aboard merchant and naval vessels, including service in the U.S. Navy during the Civil War.
|
 Selective Service Act (1917) Selective Service Act (1917) |
|
This act authorized the U.S. government to raise a national army through compulsory enlistment via a draft. The military was segregated at the time of World War I, and Black soldiers were mostly relegated to labor roles.
|
 Selective Training and Service Act (1940) Selective Training and Service Act (1940) |
|
This act authorized the U.S. government to raise a national army through compulsory enlistment via a draft. While the act prohibited discrimination based on race, the military was still segregated at the time of World War II, and Black soldiers were mostly relegated to labor roles.
|
 Seminole Agreement (1900) Seminole Agreement (1900) |
|
This congressional act ratified an agreement with the Seminole Nation concerning allotment, like enrollment and laws of descent. The second proviso established matrilineal descent of lands, money, and property for heirs.
|
 Separate schools for white and colored (1904) Separate schools for white and colored (1904) |
|
Acts passed by the Virginia General Assembly reflected race-neutral language of the legal code after the Civil War. Application of these statutes resulted in entrenched Jim Crow segregation.
|
 She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020) She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020) |
|
This essay refocuses the story of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay on Charlotte herself, detailing her long struggle navigating the strategies and pathways to freedom.
|
 Shelby County v. Holder (2013) Shelby County v. Holder (2013) |
|
This landmark Supreme Court decision overturned the federal pre-clearance section the Voting Rights Act of 1965 which required jurisdictions to seek approval from the Department of Justice or the U.S. District Court for D.C., before making changes to their voting laws. This decision limited the federal government's ability to protect voting rights for all citizens and has since allowed policies such as voter ID laws and the closing polling locations to limit voting rights for certain groups.
|
 Shelley v. Kraemer (1948) Shelley v. Kraemer (1948) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court ruled that the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment prohibited the enforcement of restrictive covenants banning the purchase or occupation of property based on race. Shelley v. Kraemer was decided alongside Hurd v. Hodge, which held that the Civil Rights Act of 1866 prohibits judicial enforcement by D.C. courts of such restrictive covenants.
|
 Slaves and Free Negroes (1849) Slaves and Free Negroes (1849) |
|
This act passed by the Virginia General Assembly reflects the racialization of the antebellum legal code.
|
 Smith v. Directors of Independent School Dist. of Keokuk (1875) Smith v. Directors of Independent School Dist. of Keokuk (1875) |
|
In this case, the Iowa Supreme Court affirmed a lower court's ruling that the Keokuk school district could not refuse to admit a Black student based on race. Legal precedent for this case as set in the 1868 ruling in Clark v. Board of School Directors.
|
 Somerset v. Stewart (1772) Somerset v. Stewart (1772) |
|
This case heard before the English Court of King's Bench determined that slavery was unsupported by English Common Law and that no enslaved person could be forced out of England to be sold into slavery. James Sommerset was an enslaved person who had been purchased by Charles Stewart in Boston, Massachusetts, then taken to England. Sommerset later escaped, and Stewart had him captured and imprisoned on a ship headed to Jamaica. Sommerset's godparents applied for a writ of habeas corpus. Following the court’s decision, enslaved people in the American Colonies filed freedom suits based on Mansfield's ruling.
|
 State of Iowa v. Katz (1949) State of Iowa v. Katz (1949) |
|
In this case, the Iowa Supreme Court upheld a lower court's jury verdict that Katz Drug Store violated the civil rights of three Black patrons when workers refused to serve them at the store's soda fountain.
|
 State of Missouri v. Celia (1855) State of Missouri v. Celia (1855) |
|
In this case, eighteen-year-old Celia was convicted of murdering her enslaver. The case considered whether Celia was guilty of murder or if she could be acquitted due to self-defense from sexual assault. The court ruled that Celia's enslaved status prevented her from being eligible to protect herself, and she was sentenced to death.
|
 Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854) Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854) |
|
The parties in Dred Scott v. Sandford agreed to a "Statement of Facts" about the timeline of events in Scott's life that were relevant to his freedom suit. This agreed upon evidence downplayed Dred Scott's active role in putting his case before the court.
|
 Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894) Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894) |
|
This statement prepared by members of the Committee of Chickasaw Freedmen's Association recounts how the Chickasaw Nation had not met its treaty obligations to Chickasaw Freedpeople.
|
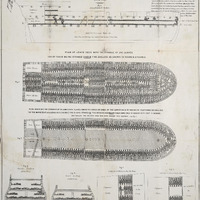 Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) |
|
This image was used by English abolitionists to demonstrate the terrible conditions aboard slave ships.
|
 Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971) Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court addressed busing as a means of integrating schools. After a federal district court found that the North Carolina school system's zoning-based desegregation plan was ineffectual, the court appointed an expert to develop an alternative plan. The new plan required the busing of students to various schools in order to achieve desegregation, which the Supreme Court held as an acceptable "remedial technique" to that end. The decision was eventually abrogated in Belk v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education (2002), where the court found that the previously instituted remedial techniques had been successful and were no longer necessary.
|
 Sweatt v. Painter (1950) Sweatt v. Painter (1950) |
|
In this case, the Supreme Court held that separate Black law schools in Texas were not equal in quality to white-only law schools. Sweatt v. Painter set important precedent for the decision in Brown v. Board of Education four years later.
|
 Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) |
|
In this sworn affidavit, Alexander Harlin attested that he, as a "Choctaw Freedman, of African Blood," was enslaved by a Choctaw woman Sarah Harlin until the Treaty of 1866 was signed. The statement was made in support of his application for enrollment in the Choctaw Nation under the Act of June 10, 1896 which authorized the Dawes Commission to add names to existing tribal rolls.
|
 Sworn Affidavit of Jeff Franklin Regarding His Enslavement and Emancipation in the Chickasaw Nation as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Chickasaw (1896) Sworn Affidavit of Jeff Franklin Regarding His Enslavement and Emancipation in the Chickasaw Nation as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Chickasaw (1896) |
|
In this sworn affidavit, Jeff Franklin attested that he was a colored man and was enslaved by Easter Colber, a Chickasaw man until April 28th, 1866, when the Treaty of 1866 was signed. The statement was made in support of his application for enrollment in the Chickasaw Nation under the Act of June 10, 1896 which authorized the Dawes Commission to add names to existing tribal rolls. The affidavit also includes information about his continued residency in the Chickasaw Nation until the time of his application in 1896.
|
 Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) |
|
In this sworn statement, W. L. Cochran attested that Margaret Clark, "an African woman," was enslaved by R. L. Cochran in the Choctaw Nation until the Treaty of 1866 was signed. The statement was made in support of Margaret Clark's application for enrollment in the Choctaw Nation under the Act of June 10, 1896 which authorized the Dawes Commission to add names to existing tribal rolls.
|
 Terry v. Ohio (1968) Terry v. Ohio (1968) |
|
Terry v. Ohio is the landmark Supreme Court case that established the basis for stop and frisk policies. These policies disproportionately affect Black people and lead to the disproportionate incarceration of Black Americans.
|
 Texas Poll Tax (1901) Texas Poll Tax (1901) |
|
This poll tax law in Texas was voted on in a referendum in the 1902 election as a proposed amendment to the state constitution.
|
 Remembering a dark past, renewing resolve for the future (2019)
Remembering a dark past, renewing resolve for the future (2019) Rights of Black Men (1791)
Rights of Black Men (1791) Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810)
Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810) Selective Service Act (1917)
Selective Service Act (1917) Selective Training and Service Act (1940)
Selective Training and Service Act (1940) Seminole Agreement (1900)
Seminole Agreement (1900) Separate schools for white and colored (1904)
Separate schools for white and colored (1904) She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020)
She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020) Shelby County v. Holder (2013)
Shelby County v. Holder (2013) Shelley v. Kraemer (1948)
Shelley v. Kraemer (1948) Slaves and Free Negroes (1849)
Slaves and Free Negroes (1849) Smith v. Directors of Independent School Dist. of Keokuk (1875)
Smith v. Directors of Independent School Dist. of Keokuk (1875) Somerset v. Stewart (1772)
Somerset v. Stewart (1772) State of Iowa v. Katz (1949)
State of Iowa v. Katz (1949) State of Missouri v. Celia (1855)
State of Missouri v. Celia (1855) Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854)
Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854) Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894)
Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788)
Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971)
Swann et al. v. Charlotte-Mecklenburg Board of Education et al. (1971) Sweatt v. Painter (1950)
Sweatt v. Painter (1950) Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896)
Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Affidavit of Jeff Franklin Regarding His Enslavement and Emancipation in the Chickasaw Nation as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Chickasaw (1896)
Sworn Affidavit of Jeff Franklin Regarding His Enslavement and Emancipation in the Chickasaw Nation as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Chickasaw (1896) Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896)
Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Terry v. Ohio (1968)
Terry v. Ohio (1968) Texas Poll Tax (1901)
Texas Poll Tax (1901)