 Rights of Black Men (1791) Rights of Black Men (1791) |
|
This commentary was written by Connecticut anti-slavery advocate Abraham Bishop in support of the Haitian Revolution. Bishop's work was printed in the Boston newspaper, The Argus.
|
 Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810) Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810) |
|
Seamen's Protection Certificates were documents authorized by an act of Congress in 1796 to protect U.S. sailors from being impressed into the service of foreign navies. For Black Americans, they also served as a way to document their free status. This certificate was issued for James Forten Dunbar, a free man of mixed ancestry who spent a long career at sea as a sailor and sail-maker aboard merchant and naval vessels, including service in the U.S. Navy during the Civil War.
|
 She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020) She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020) |
|
This essay refocuses the story of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay on Charlotte herself, detailing her long struggle navigating the strategies and pathways to freedom.
|
 Slaves and Free Negroes (1849) Slaves and Free Negroes (1849) |
|
This act passed by the Virginia General Assembly reflects the racialization of the antebellum legal code.
|
 Somerset v. Stewart (1772) Somerset v. Stewart (1772) |
|
This case heard before the English Court of King's Bench determined that slavery was unsupported by English Common Law and that no enslaved person could be forced out of England to be sold into slavery. James Sommerset was an enslaved person who had been purchased by Charles Stewart in Boston, Massachusetts, then taken to England. Sommerset later escaped, and Stewart had him captured and imprisoned on a ship headed to Jamaica. Sommerset's godparents applied for a writ of habeas corpus. Following the court’s decision, enslaved people in the American Colonies filed freedom suits based on Mansfield's ruling.
|
 State of Missouri v. Celia (1855) State of Missouri v. Celia (1855) |
|
In this case, eighteen-year-old Celia was convicted of murdering her enslaver. The case considered whether Celia was guilty of murder or if she could be acquitted due to self-defense from sexual assault. The court ruled that Celia's enslaved status prevented her from being eligible to protect herself, and she was sentenced to death.
|
 Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854) Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854) |
|
The parties in Dred Scott v. Sandford agreed to a "Statement of Facts" about the timeline of events in Scott's life that were relevant to his freedom suit. This agreed upon evidence downplayed Dred Scott's active role in putting his case before the court.
|
 Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894) Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894) |
|
This statement prepared by members of the Committee of Chickasaw Freedmen's Association recounts how the Chickasaw Nation had not met its treaty obligations to Chickasaw Freedpeople.
|
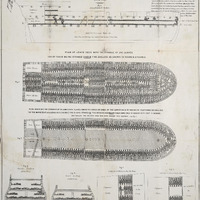 Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) |
|
This image was used by English abolitionists to demonstrate the terrible conditions aboard slave ships.
|
 Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) |
|
In this sworn affidavit, Alexander Harlin attested that he, as a "Choctaw Freedman, of African Blood," was enslaved by a Choctaw woman Sarah Harlin until the Treaty of 1866 was signed. The statement was made in support of his application for enrollment in the Choctaw Nation under the Act of June 10, 1896 which authorized the Dawes Commission to add names to existing tribal rolls.
|
 Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) |
|
In this sworn statement, W. L. Cochran attested that Margaret Clark, "an African woman," was enslaved by R. L. Cochran in the Choctaw Nation until the Treaty of 1866 was signed. The statement was made in support of Margaret Clark's application for enrollment in the Choctaw Nation under the Act of June 10, 1896 which authorized the Dawes Commission to add names to existing tribal rolls.
|
 The Slave, Grace (1827) The Slave, Grace (1827) |
|
In this freedom suit, an enslaved woman who had spent time in England was re-enslaved once she voluntarily returned to her home in Antigua. The court found that while she became free once she set foot on English soil, her status reverted to that of enslaved once she returned to Antigua.
|
 The Timing of Queen v. Hepburn: An exploration of African American Networks in the Early Republic (2015) The Timing of Queen v. Hepburn: An exploration of African American Networks in the Early Republic (2015) |
|
This essay explores the phenomenon of multigenerational networks of freedom-making through the petition for freedom cases of the Queen family in Washington, D.C.
|
| The Treaty of 1866 and the Long Fight for Black Belonging in the Choctaw and Chickasaw Nations |
|
This module reframes histories of the Civil War, emancipation, and Reconstruction by analyzing how enslaved and freed Black people in the Choctaw and Chickasaw Nations struggled to actualize their freedoms amid contested tribal and federal jurisdictions. Ultimately, the module elucidates how Black enslaved and Freedpeople in the Chickasaw and Choctaw Nations developed unique methods of resistance and visions of freedom shaped by the legal paradigms forged in the Treaty of 1866.
|
 Treaty with the Choctaw and Chickasaw (1866) Treaty with the Choctaw and Chickasaw (1866) |
|
The 1866 Treaty with the Choctaw and Chickasaw was one of a series of treaties between the United States government and each of the "Five Civilized Tribes" (the Cherokee, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Muscogee Creek, and Seminole Nations) at the end of the Civil War. The treaty details the stipulations for the Choctaw and Chickasaw Nations to re-establish their allegiance with the U.S. after allying with the Confederate States of America during the Civil War. Among other provisions, the Choctaw and Chickasaw Treaty of 1866 included articles that outlawed slavery within both nations (except as a punishment for crime), provided a pathway for citizenship and civil rights for the Freedmen of both nations, and ceded lands to the United States.
|
 Unis et al. v. Charlton's Administrator et al. (1855) Unis et al. v. Charlton's Administrator et al. (1855) |
|
In this freedom suit, the descendants of a Black woman named Flora claimed their freedom on the grounds that Flora was free before being abducted and sold into slavery in Virginia. Between 1826-1855, a series of cases bounced around county and appellate courts in Virginia before finally being decided against freedom for Flora's descendants.
|
 United States v. The Amistad (1841) United States v. The Amistad (1841) |
|
This freedom suit originated after 53 Africans revolted and took control of the Spanish slave ship that intended to enslave them in Cuba. The ship was eventually seized by the U.S. Navy off the coast of Long Island and the Africans were taken into custody and charged with mutiny and murder. After a series of court appearances, the Supreme Court ruled that the Africans were "free negroes" who had been "unlawfully kidnapped, and forcibly and wrongfully carried on board" the Amistad. They were ordered to be released. After obtaining their freedom, missionary groups helped the surviving Africans return to Sierra Leone.
|
 Winny v. Phebe Whitesides alias Prewitt (1824) Winny v. Phebe Whitesides alias Prewitt (1824) |
|
This case was the first freedom suit heard by the Missouri Supreme Court. Winny claimed her freedom on account of being brought into the free territory of what would become Illinois before being removed to Missouri. The court found in favor of her freedom, establishing a "once free, always free" precedent that was eventually overturned by the decision in Dred Scott v. Sandford.
|
 Rights of Black Men (1791)
Rights of Black Men (1791) Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810)
Seamen's Protection Certificate for James Forten Dunbar (1810) She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020)
She's Been Her Own Mistress: The Long History of Charlotte Dupee v. Henry Clay, 1790-1840 (2020) Slaves and Free Negroes (1849)
Slaves and Free Negroes (1849) Somerset v. Stewart (1772)
Somerset v. Stewart (1772) State of Missouri v. Celia (1855)
State of Missouri v. Celia (1855) Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854)
Statement of Facts in Dred Scott v. Sanford (1854) Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894)
Statement of the Chickasaw Freedmen, Setting Forth Their Wrongs, Grievances, Claims and Needs (1894) Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788)
Stowage of the British slave ship "Brookes" under the Regulated Slave Trade Act (1788) Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896)
Sworn Affidavit of Alexander Harlin Regarding His Continued Enslavement Until the 1866 Treaty as Part of His Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896)
Sworn Statement of W. L. Cochran as to the Enslavement of Margaret Clark in 1866 in Support of Her Application for Enrollment as a Choctaw (1896) The Slave, Grace (1827)
The Slave, Grace (1827) The Timing of Queen v. Hepburn: An exploration of African American Networks in the Early Republic (2015)
The Timing of Queen v. Hepburn: An exploration of African American Networks in the Early Republic (2015) Treaty with the Choctaw and Chickasaw (1866)
Treaty with the Choctaw and Chickasaw (1866) Unis et al. v. Charlton's Administrator et al. (1855)
Unis et al. v. Charlton's Administrator et al. (1855) United States v. The Amistad (1841)
United States v. The Amistad (1841) Winny v. Phebe Whitesides alias Prewitt (1824)
Winny v. Phebe Whitesides alias Prewitt (1824)